All the pictures in this post are coming from the video: 花花酱 LeetCode Binary Search - 刷题找工作 SP5
- Summary
- What is Binary Search?
- Why we need Binary Search.
- Template
- Relative Questions
Summary
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding an item from a sorted list of items. It works by repeatedly dividing in half the portion of the list that could contain the item, until you've narrowed down the possible locations to just one.
For example, binary search in the guessing game. Here, try it for a number from 1 to 300. You should need no more than 9 guesses.
Here's a step-by-step description of using binary search to play the guessing game:
- Let min = 1 min=1 and max = nmax=n.
- Guess the average of maxmax and minmin, rounded down so that it is an integer.
- If you guessed the number, stop. You found it!
- If the guess was too low, set minmin to be one larger than the guess.
- If the guess was too high, set maxmax to be one smaller than the guess.
- Go back to step two.
The feature for the Binary Search is: Fast, Fast, Fast. O(log(n))
What is Binary Search?

The requirment for the Binary Search is the sorted input data.
Each node needs to make decision go to left or right. For the Binary Search method, the input data will include three partition: Mid, left array, right array.
- If the mid number is less than the target number, then go to right array to find the target number.
- If the mid number is larger than the target number, then go to left array to find the target number.
When you go to the left or right way, you can choose the recursive function or not recursive function to solve it.
The answer for this question is that the last mid point is the target number which you want to find if there is a target number in the array. If there is no target number in the array, when you find the last mid number and then you can return false or use this number to do something.
Why we need Binary Search.
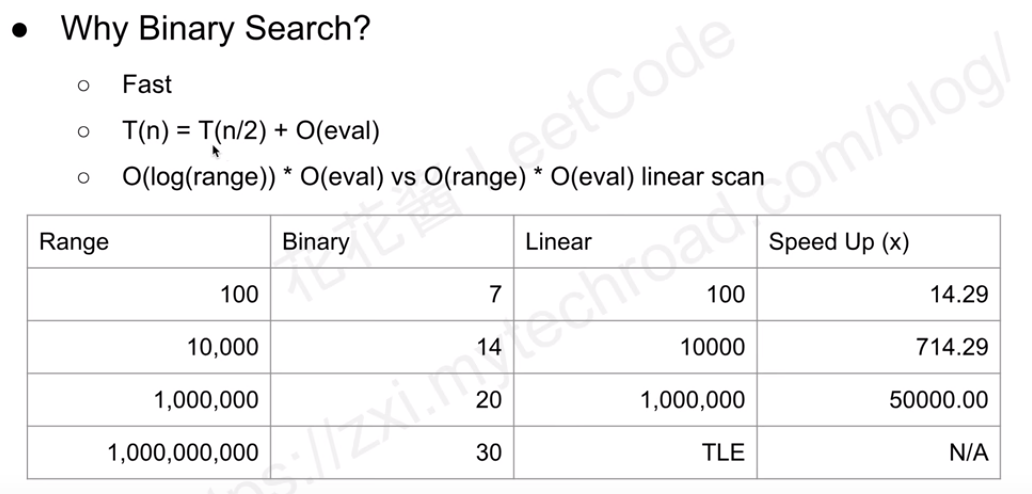
There are some states for the above picture:
- The O(eval) is the time to compare the mid number with the target number and the search space need to move to left part or right part. It may be: O(1), O(n), or O(logn).
SO, you can use the input dataset range to choose which mothod you can use to solve this problem. There are two tips which you can use to think which method is good for you to solve this problem.
Template
Template 1: Unique and sorted elements
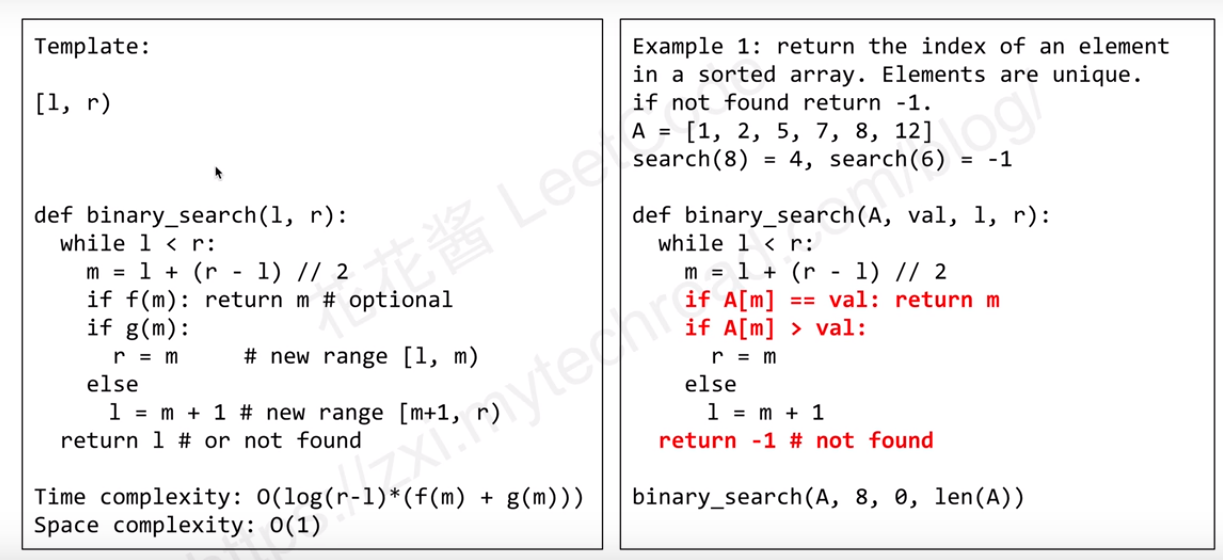
Include the left data, but not include the right side.
def binary_search(1,r):
while l < r:
m = 1 + (r-1) // 2
if f(m): return m #optional
if g(m):
r = m
else:
l + m + 1
return l #or not find, return the min number
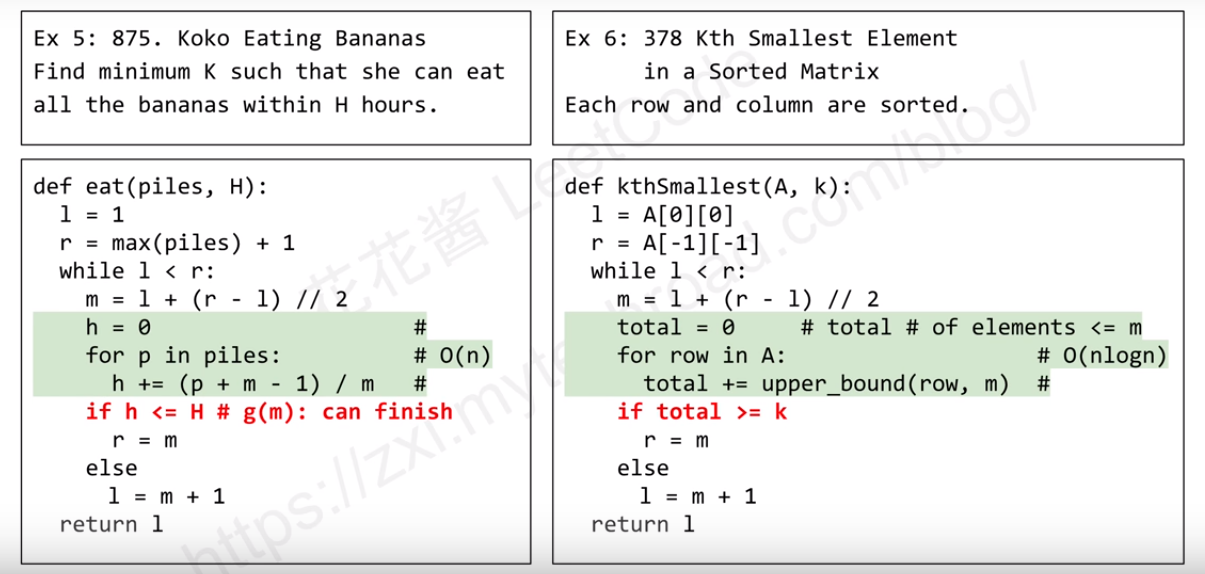
As the above picture, if the input element is unique and sorted, then we can easily use this template to deal with these similar problems. Like the example 1.
If the Input data's element is not unique. And it have repetitive numbers.
Template 2: Repetitive and sorted elements
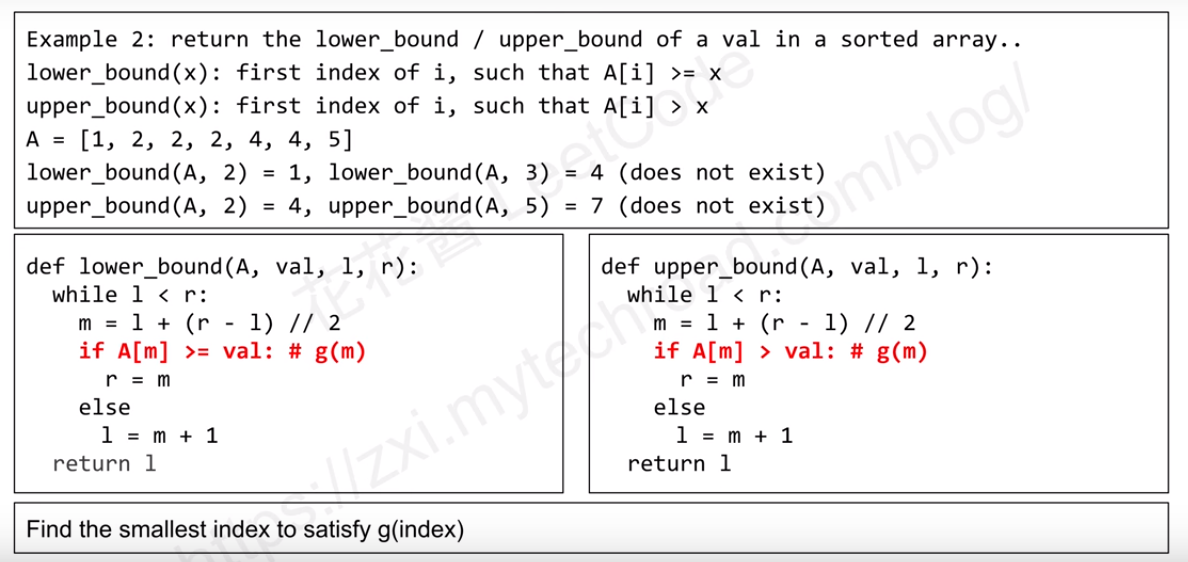
The lower_bound function will return the first index of i, such that A[i] >= x, So, when you find it, you need to check out if this A[i] may not = x. If the index > len, then there is no number > this.
Example
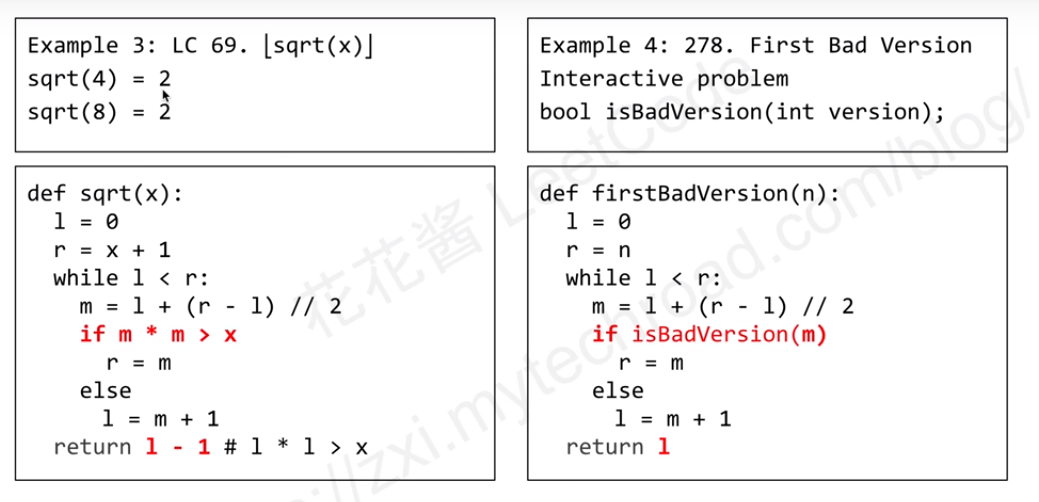
Leetcode 69
It is not way to find the real number to fit the requrtment. So, we can find the number the first time bigger than the input.
Relative Questions
二分查找算法在实际使用中可能会出现各种变体,我们要抓住有序的特点,一旦发现输入有有序的特点,我们就可以考虑是否可以运用二分查找算法来解决该问题。
Questions:
- Search In Rotated Sorted Array
- Search In Rotated Sorted Array II
- Search Insert Position
- Online Election
- Preimage Size of Factorial Zeroes Function
- K th Smallest Prime Fraction
- Find Smallest Letter Greater Than Target
- Find K th Smallest Pair Distance
- Relative Ranks
- Find K th Smallest Pair Distance
- Search a 2D Matrix
- Sqrt x 3
Upper Bound
Find First And Last Position Of Element In Sorted Array(LC.34)
问题:在一个有序的数组中,找到一个元素的第一个位置以及最后一个位置。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int> res(2, -1);
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid;
}
if (nums[right] != target) return res;
res[0] = right;
// Do the second Binary Search
right = nums.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] <= target)
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid;
}
res[1] = left - 1;
return res;
}
};
Search Insert Position(LC.35)
在一个有序数组中找到一个位置,插入 target 的数字,插入之后,数组依旧保持有序
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
if (nums.back() < target) return nums.size();
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid;
}
return right;
}
};
Binary Search(LC.704)
Problem: Given a sorted (in ascending order) integer array nums of n elements and a targetvalue, write a function to search target in nums. If target exists, then return its index, otherwise return -1.
Time complexity: O(log n), Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return -1;
}
};
Time Based Key Value Store(LC.981)
Solution: HashTable + Map
class TimeMap {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
TimeMap() {}
void set(string key, string value, int timestamp) {
s_[key].emplace(timestamp, std::move(value));
}
string get(string key, int timestamp) {
auto m = s_.find(key);
if (m == s_.end()) return "";
auto it = m->second.upper_bound(timestamp);
if (it == begin(m->second)) return "";
return prev(it)->second;
}
private:
unordered_map<string, map<int, string>> s_;
};
Sqrt x 3(LC.69)
Time Complexity: O(log n), Space Complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int mySqrt(int x) {
if (x < 2) return x;
int left = 0, right = x / 2 + 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// Move left == right, then we need to move left back
x / mid < mid ? right = mid : left = mid + 1;
}
return left - 1;
}
};
Rotated & Peak
Search In Rotated Sorted Array(LC.33)
Time complexity: O(log n) Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size();
while (left != right) {
const int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// Find the Target at the mid index.
if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
// There are sorted elements in the left part.
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
nums[mid] > target && nums[left] <= target ? right = mid : left = mid + 1;
} else {
nums[mid] < target && nums[right - 1] >= target ? left = mid + 1 : right = mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
Search In Rotated Sorted Array II(LC.81)
Time complexity: O(logn) Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
bool search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size();
while (left != right) {
const int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// Find the Target at the mid index.
if (nums[mid] == target) return true;
// There are sorted elements in the left part.
if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
if (nums[left] <= target && nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else if (nums[left] == nums[mid]) {
left++;
} else { // There are sorted elements in the right part.
if (nums[mid] < target && nums[right - 1] >= target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array(LC.153))
Time Complexity: O(log n), Space Complexity:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
if (nums[left] < nums[right]) return nums[0];
while (left < right - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// If the mid value > left value, then move the right part search.
if (nums[mid] > nums[left]) left = mid;
else right = mid;
}
return min(nums[left], nums[right]);
}
};
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II(LC.154)
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1, ans = nums[0];
if (nums[left] < nums[right]) return nums[0];
while (left < right - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// If the mid value > left value, then move the right part search.
if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
ans = min(ans, nums[left]);
left = mid;
}
else if (nums[left] > nums[mid]) right = mid;
else ++left;
}
return min(ans, min(nums[left], nums[right]));
}
};
Find Peak Element(LC.162)
题目要求是 O(log n) 的时间复杂度,考虑使用类似于二分查找法来缩短时间。由于只是需要找到任意一个峰值,那么我们在确定二分查找折半后中间那个元素后,和紧跟的那个元素比较下大小,如果大于,则说明峰值在前面,如果小于则在后面。这样就可以找到一个峰值了。
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& A) {
// Binary Search
int left = 0, right = A.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (A[mid] < A[mid + 1]) left = mid + 1; // For the left part
else right = mid;
}
return left;
}
};
Peak Index in a Mountain Array(LC.852)
Time complexity: O(log n), Space Complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int peakIndexInMountainArray(vector<int>& A) {
// Binary Search
int left = 0, right = A.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (A[mid] > A[mid + 1]) right = mid; // For the left part
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
};