Question
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
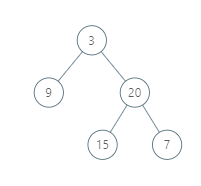
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0): Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1); The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2); The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1); The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
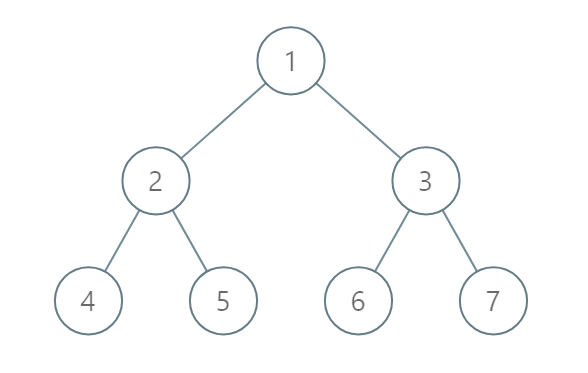
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme. However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
Difficulty:Medium
Category:Tree
Analyze
题目要求遍历二叉树,并把每一列存入一个二维数组,我们应该如何来确定列的顺序呢? 在列内部, 我们又如何确定顺序呢?
我们可以把根节点给个序号0,然后开始层序遍历,凡是左子节点则序号减1,右子节点序号加1,这样我们可以通过序号来把相同列的节点值放到一起,我们用一个TreeMap来建立序号和其对应的节点值的映射,用TreeMap的另一个好处是其自动排序功能可以让我们的列从左到右,由于层序遍历需要用到queue,我们此时queue里不能只存节点,而是要存序号和节点组成的pair,这样我们每次取出就可以操作序号,而且排入队中的节点也赋上其正确的序号
Solution
Solution 1: Ordered_Map + Ordered_set
Time complexity: O(nlogn) Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {};
int min_col = INT_MAX;
int max_col = INT_MIN;
// Sort by the row value in the map, second sort by the col value
// In the set, sort by the value
map<pair<int, int>, set<int>> rec; // {row, col} -> {vals}
traverse(root, 0, 0, rec, min_col, max_col);
vector<vector<int>> ans(max_col - min_col + 1); // max_x - min_x = number of the col
for (const auto& m : rec) {
int x = m.first.second - min_col; // Get the col val and map to ans
// Insert the elements at the last of the vector.
ans[x].insert(ans[x].end(), m.second.begin(), m.second.end());
}
return ans;
}
private:
void traverse(TreeNode* root, int col, int row, map<pair<int, int>, set<int>>& rec, int& min_col, int& max_col) {
if (!root) return;
min_col = min(min_col, col);
max_col = max(max_col, col);
rec[{row, col}].insert(root->val);
traverse(root->left, col - 1, row + 1, rec, min_col, max_col);
traverse(root->right, col + 1, row + 1, rec, min_col, max_col);
}
};
Solution 2: Recursive
Runtime: 12 ms, faster than 93.08% of C++ online submissions for Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree. Memory Usage: 16.6 MB, less than 18.02% of C++ online submissions for Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree.
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
recurse(root, 0, 0);
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (const auto& column : ans) {
res.push_back(vector<int>());
for (const auto& cell : column.second) {
for (const auto& number : cell.second) {
res.back().push_back(number);
}
}
}
return res;
}
void recurse(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
ans[x][y].insert(root->val);
recurse(root->left, x - 1, y + 1);
recurse(root->right, x + 1, y + 1);
}
map<int, map<int, set<int>>> ans;
};
Solution 3: Iteration (Error)
这种做法没有考虑列里面的顺序,可用在 Leetcode 314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (!root) return res;
map<int, vector<int>> m;
queue<pair<int, TreeNode*>> q;
q.push({0, root});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto a = q.front();
q.pop();
m[a.first].push_back(a.second->val);
if (a.second->left) q.push({a.first - 1, a.second->left});
if (a.second->right) q.push({a.first + 1, a.second->right});
}
for (auto a : m) {
res.push_back(a.second);
}
return res;
}
};