Cloud computing Basic concepts
Exam 1 Review Questions. Exam 1 will be derived from these questions.
注明:加粗的问题是考试的重点考试题目
Acronyms Expand each of the following acronyms of the following in the context of this class:
- AWS: Amazon Web Services
- AZ: Availablity Zone
- EC2: Elastic Compute Cloud
- S3: Sample Storage Service
- EBS: Elastic Block Store
- RDS: Relation Database Service
- NoSQL: No-relation SQL
- ELB: Elastic Load Balancing
- PAAS: Platform as a service
- HAAS: Hardware as a service
- IAAS: Infrastructure as a service
- SAAS: Software as a service
- CIDR: Classless inter-domain routing
- REST: Representational State Transfer
- SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol
- VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
- CTO: Chief Technology Officer
- CIO: Chief Information Officer
- AMI: Amazon Machine Image
- IAM: Identity and Access Management
- MFA: Multi-factor Authentication
- IOPS: I/O Operations per second
- ACL: Access Control List
- CLI: Command Line Interface
- SDK: Software Development Kit
- API: Application Interface
- JSON: JavaScript Object Notation
General Questions
- Define cloud computing.
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the internet, with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g. networks, servers, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Name and briefly describe six advantages and benefits of using commercial cloud computing.
- No upfront investment, users just click to order resources and can be immediate access and pay for the resources you need, which are available almost immediately.
- Low on-going costs, AWS is continually lower prices and can optimize cost with prices option
- Focus on innovation, users just need to focus on application development and do not care of other operations
- Flexible capacity, you just provision the resources you need
- Speed and agility, AWS is fast and on-demand provisioning. makes it possible for you to respond to changing market conditions.
- Global reach on demand, users can deploy any AWS region on-demand and lower latency to distributed users bases.
Second
- Trade Capital Expense for Variable Expense
- Benefit from massive economies of scale.
- Stop guessing about capacity.
- Increase speed and agility.
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers.
- Go global in minutes.
What are the two cloud deployment models? All-in Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, Private Cloud(On-premises).
Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Community Cloud and Hybrid Cloud.Explain the difference between a hybrid cloud deployment model and an All-In cloud deployment model.
- All-In” Cloud is a cloud-based application that is
fully deployed in the cloud, and all parts of the application run in the cloud. - A hybrid deployment is a way to
connect infrastructure and applications between cloud-based resources and existing resourcesthat are not located in the cloud.
- All-In” Cloud is a cloud-based application that is
When was the AWS cloud first made available as a product? 2004
Name three other commercial clouds in addition to AWS. Google Engine, Mircosoft Azure, Sun Cloud.
True or False: Deploying your enterprise applications in the AWS cloud is cheaper than running your own data center. Explain your answer. True. If you running your applications in your own data center, the first thing is you must build a data center, you need to build the basic infrastructure(Power system, engine room etc.) and you need to buy lots of servers and network devices. Moreover, you must employ people to help you to maintain and manage the datacenter. But, for AWS, you just pay for the resource that you truly want and there are lots of purchases options to use AWS service.
Describe three advantages and one disadvantage of running enterprise applications in the commercial cloud as compared to running your own data center.
- Advantages: Cheaper, scalable, no labor maintain
- Disadvantage: Risk of AWS service down
AWS Computing
What is the AWS Marketplace? AWS Marketplace is an online store where you can buy or sell software that runs on Amazon Web Services.
What is a hypervisor and what is its main function? Do you have access to the hypervisor layer in AWS? Explain your answer.
- A hypervisor is a function which abstracts and isolates operating systems and applications from the underlying computer hardware. This abstraction allows the underlying host machine hardware to independently operate one or more virtual machines as guests, allowing multiple guest VMs to effectively share the system’s physical compute resources, such as processor cycles, memory space, network bandwidth and so on.
- The main function of hypervisor is to manage the virtual machines.
- No, you don’t need to access the hypervisor layer, you just need to use EC2 instance to develop your own application, and AWS will help you to manage the resource that your virtual machines needed.
What is an Instance?
Amazon instances are virtualized servers or virtual computing environments in amazon’s data centers.
- Draw the EC2 instance life cycle diagram. See here (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site.
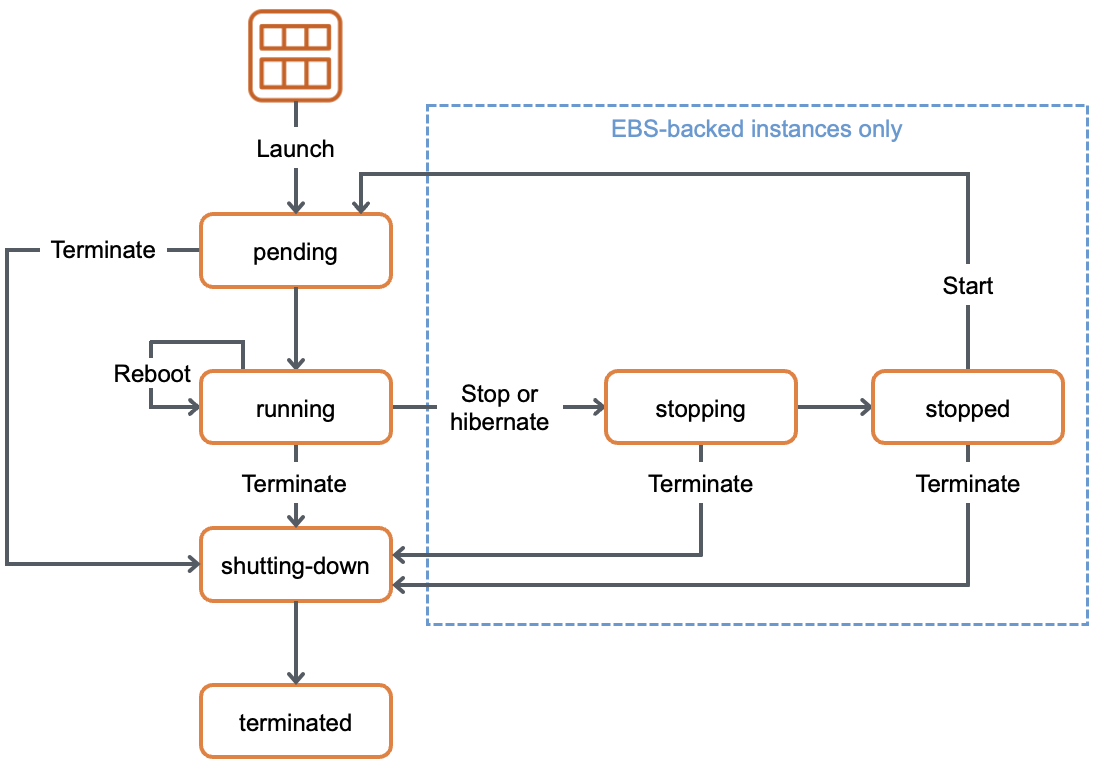
Explain what “Pay as you Go” means. “Pay as you Go” means you just pay for the resources that you truly used, and if you do not use those resources, you do not need to pay. Like electric power or water, when you use it, then you pay for it.
List four AWS EC2 Purchasing Options. On-demand instance, Reserved instance, Spot instance, Dedicated Hosts.
Scheduled instance, Dedicated instance,Describe at least three differences between On-Demand purchasing and Reserved Instance purchasing. (Between On-Demand purchasing and Spot Instance purchasing, between Reserved purchasing and Scheduled purchasing.)
- On-Demand Instances: 1. Computer capacity by the hours & second. 2. It has short-term, spiky o unprecdictable workload. Low cost and flexibility.
- Reserved Instance: 1. Purchasing need upfront payment, steady-state workload, can get 50%-75% lower than on-demand rate. 2. Overall cost is lower. 3. Predictability ensures compute capacity is available when needed.
- Spot Instances: 1.Bid for unused Amazon EC2 capacity. 2.The price based on supply and demand. 3.Instances can be lost if you’re outbid, 4. Instances can be interrupted if the Spot price exceeds the maximum. 5.Large scale, dynamic workload.
- Dedicated Hosts: 1.Save money on licensing costs. 2.Help meet compliance and regulatory requirements.
For what kind of workload would you prefer on-Demand pricing? Spot pricing? Reserved Instance pricing? Scheduled Instance pricing?
- On-demand: short term, spiky or unpredicted workload;
- Reserved: consistent, heavy workload. Steady state or preictable usage workloads.
- Spot: Applications with flexible start and end times.
- Scheduled: Usage and licensing tracking.
True or False: If you launch an instance using Spot pricing and it is terminated by AWS in 30 minutes then you are charged for the full hour.
False. The minimum is 60 seconds. But it are billed on one-second increments.
True or False: If you launch an instance using Spot pricing and you terminate it in 30 seconds then you are charged for the full minute.
True. The minimum of 60 second.True or False: An AMI includes a template for the root volume, launch permission that control which AWS accounts can use the AMI, and a block device mapping that specifies the volumes to attach to the instance when it is launched.
TrueName four families of EC2 instances.
- General purpouse: t2, m3, m4
- Compute-Optimized: c4,c3
- Mermory-Optimized: r3
- GPU instance: g2
What is Instance Metadata? Give an example.
Instance Metadata is data about the instance, can be used to configure and manage a running instance. For example, aim-id, ami-launch-index, private or public IP address etc.
- What is Instance User Data? Give an example.
Instance User data is a data can be passed to the instance at launch and can be used to perform common automated configuration scripts. For example:
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd24 php56 mysql55-server php56-mysqlnd
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
- Explain the concept of bootstrapping an instance.
It creates an application context that provides the runtime context for an application.
- True or False: You are able to reboot any type of instance.
True
AWS Storage
Describe three differences between Amazon EBS and Amazon EC2 Instance Store
- EBS: Data stored in EBS can persist independently of the life of instance. Storage is
persistent. Used to store higher level durable data.which can be mounted as a device to an Amazon EC2 instance.Mountable storage, Amazon EBS can only be mounted to an Amazon EC2 instance within thesame Availability Zone. - EC2 Instance Store: Data stored in EC2 Instance Store can persist only as long as the instance alive. Storage is ephemeral. Used to store temporary data.
- EBS: Data stored in EBS can persist independently of the life of instance. Storage is
True or False: Every type of instance can use EC2 Instance Store. Explain your answer. (This is a trick question).
False:Use the local instance store only for temporary data.What is the difference between ephemeral and persistent storage? Which type is EBS? Which type is S2? Which type is Instance Store?
- Persistent storage is just like a data is stored in hard disk, and will persist in this disk.
- The Ephemeral storage means the stored data always a temporary data, like cache, buffers etc. When the instance is unlived, this data will be deleted.
- EBS: persistent storage, S3: persistent storage , Instance Store: ephemeral storag
Describe the difference between Block Storage and Object Storage. Describe what happens if you change a single character in Block Storage versus what happens if you change a single character in Object Storage.
- Block Storage: File is split and stored in fixed sized blocks; Capacity can be increased by adding more nodes; Suitable for applications which require high IOPS, database, transactional data.
- Object Storage: Store virtually unlimited files; Maintain file revisions; HTTP(S) based interface; Files are distributed in different physical nodes.(from Google)
- This means that you must write whole objects at a time. If you change one small part of a file, you must rewrite the entire file in order to commit the change to Amazon S3.(U2page77)
True or false: S3 is a Block Storage system.
False. S3 is cloud object storage for the Internet where files are reachable via a restful URL.True or false: EBS is an Object Storage system.
False. EBS provides block-level storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances.True or false: S3 is a key-value object store with unlimited storage capacity. Explain your answer.
TrueFalse: An object is composed of a file and any metadata that describes that file. S3 can store an unlimited number of objects in a bucket. There is a 100-bucket limit per account and the size of an object can be up to 5 TB, and there is no limit to the size of a bucket.What is the largest size object that can be stored in S3?
5TBEBS can be compared to what real hardware device?
Hard disk(Hard drive)For what type of workload would you prefer S3? One very common use for Amazon S3 is storage and distribution of static web content and media Q: The data need to be accessed by internet.
True or False: You can back up EBS to S3. Explain your answer.
False, we only can backup EBS snapshot to S3What is an EBS Snapshot? An EBS snapshot is a point-in-time backup of your EBS volume. It is a “copy” of the data on your EBS volume. Snapshots are incremental backups, which means that only the blocks on the device that have changed after your most recent snapshot are saved
Describe the EBS volume lifecycle.
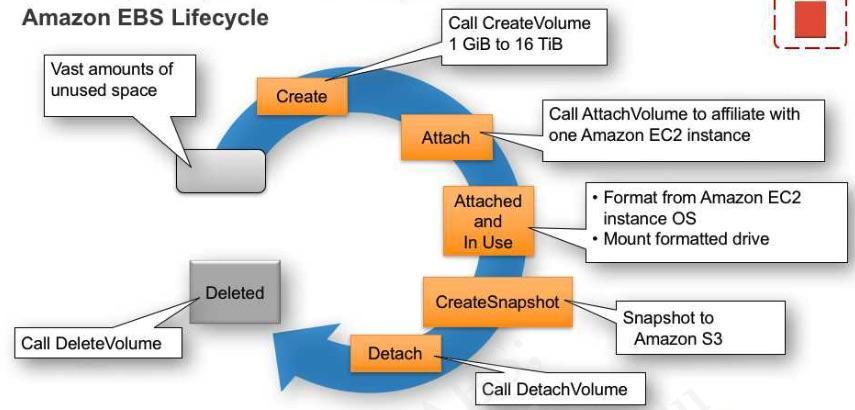
What are provisioned IOPS? Provisioned IOPS are a new EBS volume type designed to deliver predictable, high performance for I/O intensive workloads, such as database applications, that rely on consistent and fast response times
Describe three use cases for EBS. OS: use for root/boot volume, secondary volume Databases: scales with your performance needs Applications: install and persist any application
Describe the difference between Amazon S3 Standard and Amazon S3 Standard - Infrequent Access.
- Amazon S3 Standard, for general-purpose storage of frequently accessed data
- Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (Standard-IA), for long-lived, but less frequently accessed data
Data retrieval from Amazon Glacier will take _____ to begin:
- 10 minutes
- 1 hour
3-5 hours- 1-3 hours
What does it mean to be fault tolerant? Fault-tolerance defines the ability for a system to remain in operation even if some of the components used to build the system fail.
What does it mean to be highly available? High availability refers to systems that are durable and likely to operate continuously without failure for a long time.
What is the difference between availability and durability of data?
- Durability means data integrity, data is not lost etc.
- Availability means that it is “available to access”
- Data can be unavailable to access but the data will still be intact and not lost if there is high durability.
Suppose that the probability that a storage device fails in a year is 1%. Suppose that you store your data redundantly on two independent devices with the same failure rate. What is the probability that you will lose your data in a year? Assuming no use of error correcting codes, on how many devices do you have to redundantly store your data so that the probability of losing it is less than .0000000001%?
0.01%, 6How much time will an application be unavailable in a year if it has 99.999999999% availability?
0.000315s 0.019
AWS Networking
True or False: VPCs are logically isolated from other virtual networks.
TrueA VPC resides in a single:
- Availability Zone
- Edge Location
- Region
What is a data center? An Availability Zone? A Region? Give two examples of AWS regions.
- Data center: A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.
- Availability Zone: AZs consist of data centers clustered in a region.
- Region: Geographic locations that contain multiple Availability Zones.
- Two examples: US East: N. Virginia, Ohio; US West: N. California, Oregon; China: Beijing
How do Availability Zones in the same Region differ? Availability Zones are always referenced by their Code Name, which is defined by the AZs Region Code Name that the AZ belongs to, followed by a letter.
What is an Edge location? An edge location is where end users access services located on AWS platform.
True or False: There are many more Regions than Edge locations in AWS. Explain your answer.
False:74+ edge locations while 16 regionsTrue or False: Data transferred between AZs travel on private high-speed network links.
True:Each AZ is isolated, but the AZs in a region are connected through low-latency links.True or False: Data transferred between Regions travel on the public Internet.
TrueTrue or False: VPCs cannot include resources in more than one Availability Zone.
False:each subnet must reside entirely within one AZTrue or False: VPC provides various feature to provide security, including Security Groups, Network Access Control Lists, and Key Pairs.
TrueWhich of the following statements regarding Amazon VPC are True? 1,2,4
A private subnet should be used for resources that won’t be accessible over the InternetEach subnet must reside entirely within one Availability Zone- A public subnet should be used for resources that won’t be accessible over the Internet
A subnet defines a range of IP addresses in your VPC- Subnets can span Availability Zones
Each Availability Zone in an AWS Region is separated by:
At least 10s of miles- At most 10s of miles
- Exactly 10 miles
- At least 100 miles
Regions consist of at least __ Availability Zones:
- 1
- 6
2- 10
True or False: A Security Group is within a single VPC.
TrueGive an example of a network rule you might assign in a Security Group. HTTP(80), HTTPS(443)
Security Groups control both inbound and outbound traffic at the _____ level.
- Subnet
- VPC
Instance- Availability Zone
AWS Database
Describe three differences between an AWS managed service and an unmanaged service.
- Managed service offers support for every problem or task, emergency or routine versus unmanaged services offer no routine support.
- Managed service is more expensive as there is constant management versus unmanaged services are cheaper as you are responsible for everything.
- Managed hosting is far less work and requires little expertise. If something goes wrong and you’re stuck, you can call on your host to give you a hand versus Unmanaged hosting gives you complete control: sole access and total freedom.
__________ are the basic building blocks of Amazon RDS. DB instances
True or False: A DB Instance is an isolated database environment in the cloud. True: A DB instance is an isolated database environment running in the cloud. It is the basic building block of Amazon RDS.
Name four databases supported by AWS RDS. MySQL, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL
Describe three differences between using a managed RDS and building your own database on EC2. Managed RDS provide cost-efficient and resizable capacity while managing time-consuming database administration task. RDS automatically patches the database software and backs up the database. It’s flexible. It accesses to the full capabilities of databases.
In general, SQL databases have _____ scaling and NoSQL databases have _____ scaling.
verticalhorizontalDescribe the difference between vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. Horizontal scaling means that you scale by adding more machines into your pool of resources whereas vertical scaling means that you scale by adding more power (CPU, RAM) to an existing machine.
What is the main limitation to vertical scaling? That is, when can you no longer scale vertically? In Scaling Up (also known as Vertical Scaling) the limitation is hardware related in a very specific way: how much memory, disk, and processor a single server can support… Vertical scaling is limited to the capacity of a single machine.
What is the main limitation to horizontal scaling? That is, when can you no longer scale horizontally? In theory, horizontal scalability is only limited by how many entities can be connected successfully.
Give three examples of SQL-like statements.
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type);
Select * FROM table_name;
INSERT INTO table_name (field1, field2,...) VALUES (value1, value2,...);
- Give an example of datasqu that might be in a NoSQL database.
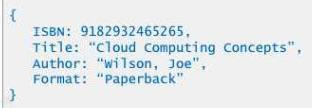
True or False: You cannot use SQL to query a NoSQL database. Explain your answer.
FalseTrue or False: You can query and scan DynamoDB to retrieve data.
TrueFor what type of workload would you prefer DynamoDB? New web-scale applications and larger number of small read and write
True/False: You should utilize Amazon DynamoDB if your application requires complex queries, joins, and updates.
FalseTrue or False: You should utilize Amazon DynamoDB if your data is unstructured and you require fast I/O.
TrueWhich of the following allows unlimited storage:
S3- EBS
- Instance Store
- RDS
DynamoDB
Describe eventually consistent reads and strongly consistent reads. Which AWS service(s) provide eventually consistent reads, and under what conditions? (Move to exam 2) service(s) provide eventually consistent reads, and under what conditions?
- Eventually Consistent Reads: When you read data from a DynamoDB table, the response might not reflect the results of a recently completed write operation. The response might include some stale data. If you repeat your read request after a short time, the response should return the latest data.
- Strongly Consistent Reads: When you request a strongly consistent read, DynamoDB returns a response with the most up-to-date data, reflecting the updates from all prior write operations that were successful. A strongly consistent read might not be available if there is a network delay or outage.
- By default (DynamoDB)
Why would we not always use strongly consistent reads in a distributed system like AWS? A strongly consistent read might not be available if there is a network delay or outage.
Describe the similarity and difference between Secondary DB and Read Replica DB
AWS Scalability
Name the two types of load balancers. Classic load balancer, Application load balancer, Network load balancer.
You can create Auto Scaling Group scaling policies that utilize _____ to determine when your Auto Scaling group should scale out or scale in. 1. VPC 2. S3 3.
CloudWatch alarms4. Instance StoreList three things that you can specify when you create a Launch Configuration.
- A key pair
- Security group
- A block device mapping The ID of the Amazon Machine Image (AMI), the instance type, a key pair, one or more security groups, and a block device mapping
List three benefits of utilizing Auto Scaling within your application.
- Better fault tolerance
- Better availability
- Better cost management
True or False: An Auto Scaling group is a collection of EC2 Instances that share the same characteristics.
True: An Auto Scaling group contains a collection of EC2 instances that share similar characteristics and are treated as a logical grouping for the purposes of instance scaling and management.Explain the concept of bootstrapping an instance. It creates an application context that provides the runtime context for an application.
AWS Security
What does “Security of the Cloud” mean? Describe three aspects of security of the cloud. The policies and mechanisms AWS use to protect the cloud itself. Compute, storage, database, networking.
What does “Security in the Cloud” mean? Describe three aspects of security in the cloud. The AWS service you utilize to run your workloads. Operating system, customer application and content, IAM
Define authentication. Define authorization. How are they different?
- Authentication is the process of verifying who you are. When you log on to a PC with a username and password you are authenticating.
- Authorization is the process of verifying that you have access to something. Gaining access to a resource (e.g. directory on a hard disk) because the permissions configured on it allow you access is authorization.
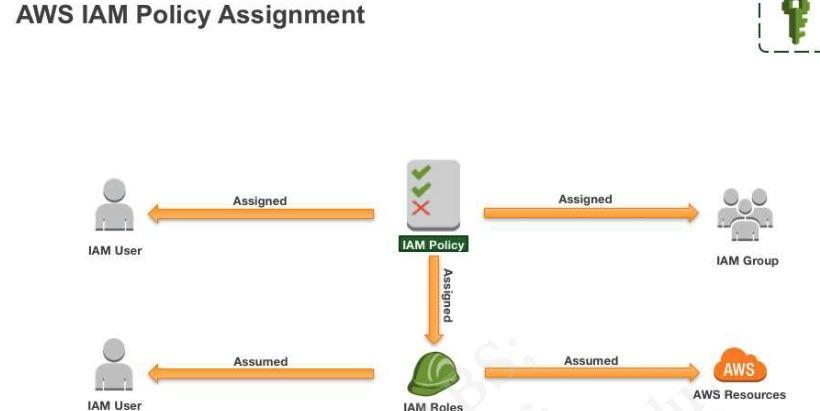
List the three IAM constructs that an IAM Policy can be assigned to. IAM users, IAM groups, IAM role.
Explain what an IAM User is. An IAM user is an entity that you create in AWS to represent the person or service that uses it to interact with AWS.
Explain a difference between role-based authorization and user-based authorization. Roles-based authorization is used to group users into groups (roles) and then set permissions on the role rather than on individual users.
True/False: All IAM permissions in AWS are implicitly allowed by default.
FalseDraw the IAM permissions flow chart.
Suppose you create a policy for a user to Allow access to a table called “Table1”. In your same policy you Deny access to any table that is Not “Table1”. Then in the same policy you Allow access to “Table2”. Can this user access “Table2”? Why or why not? Answer: The user can’t access table 2 because we can’t rewrite or overwrite the previlieges already defined. If the user needs to access it he needs to define it before its access is set as deny
IAM Policies are written in _____.
JSON- CSV
- XML
True or False: IAM is appropriate for OS and application authentication.
False